What is PON: PON is the abbreviation of Passive Optical Network. As an access network technology, PON is positioned in what is often called the "last mile" and is widely used. The system is often composed of OLT, ODN, ONU and other parts.
What is FTTX: FTTX is the abbreviation of fiber to the X, which is the collective name for the optical fiber communication network in the access network. X represents the destination of the optical fiber line.
PON network
Basic principles of PON
Basic principle: OLT and ONU are connected using a single fiber, and the downlink and uplink use different wavelengths.
Single fiber bidirectional, WDM wavelength division
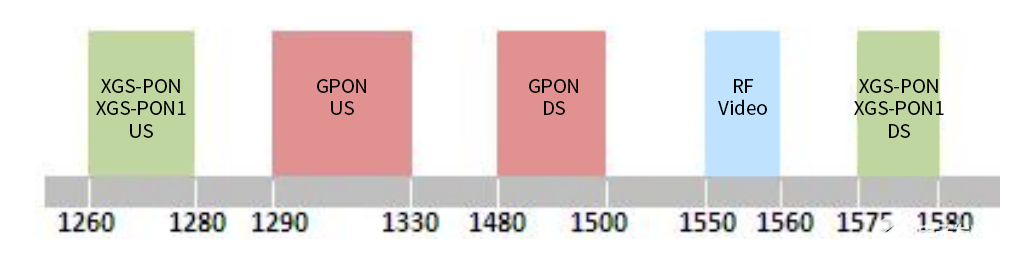
Downlink wavelength: 1490nm/1577nm
Upstream wavelength: 1310nm/1270nm
Third wavelength: 1550nm
speed class
1G, 2.5G, 10G, 40G…
Uplink and downlink symmetry and asymmetry
Downlink based on broadcast
Continuous light
ONU logo
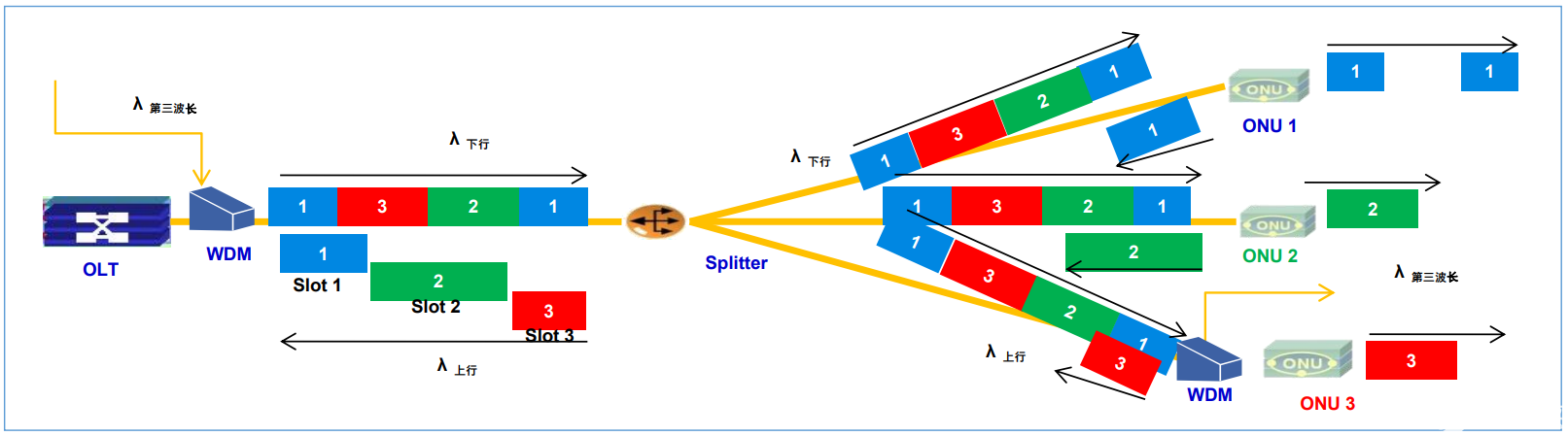
Uplink uses TDMA time division multiplexing
optical burst mode
The ONU is synchronized with the OLT, and the OLT controls the transmission time slot and bandwidth of the ONU.
Principle introduction:
The PON downstream data stream is transmitted using TDM (time-division multiplexing) broadcast mode. The ONU is assigned a unique LLID after completing registration; the upstream data stream is transmitted using TDMA (Time-Division Multiplexing Time Division Multiple Access). Before the downlink data of EPON OLT is sent out, the source will add an LLID (15bit). This LLID corresponds to one of the ONUs below. When the ONU receives the data, it will judge whether the LLID is consistent with its own at the physical layer. The LLID matches. If it matches, it is accepted. If it does not match, it is discarded. GPON uses the ONU-ID (8bit) in PLOAMd in the downlink GTC frame to distinguish different ONU data.
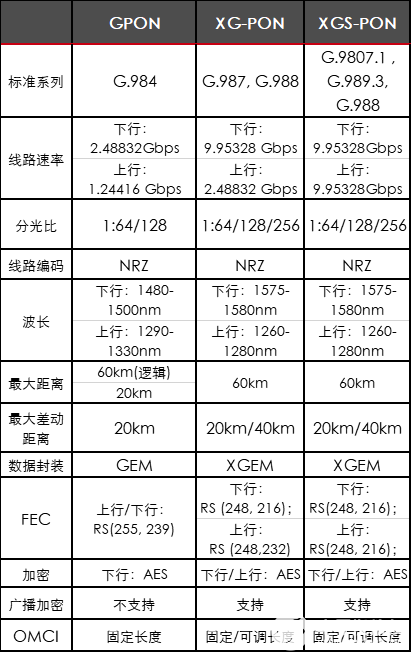
The main differences between several typical PONs
To sum up, the main differences are:
Different uplink and downlink rates
The maximum splitting ratio supported is different
Different distances supported
Different wavelengths for uplink and downlink
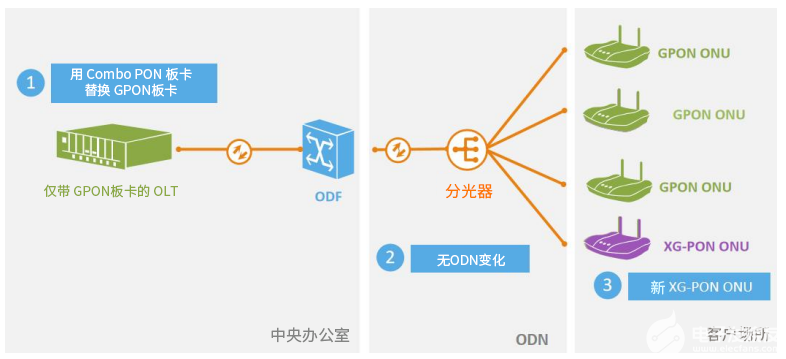
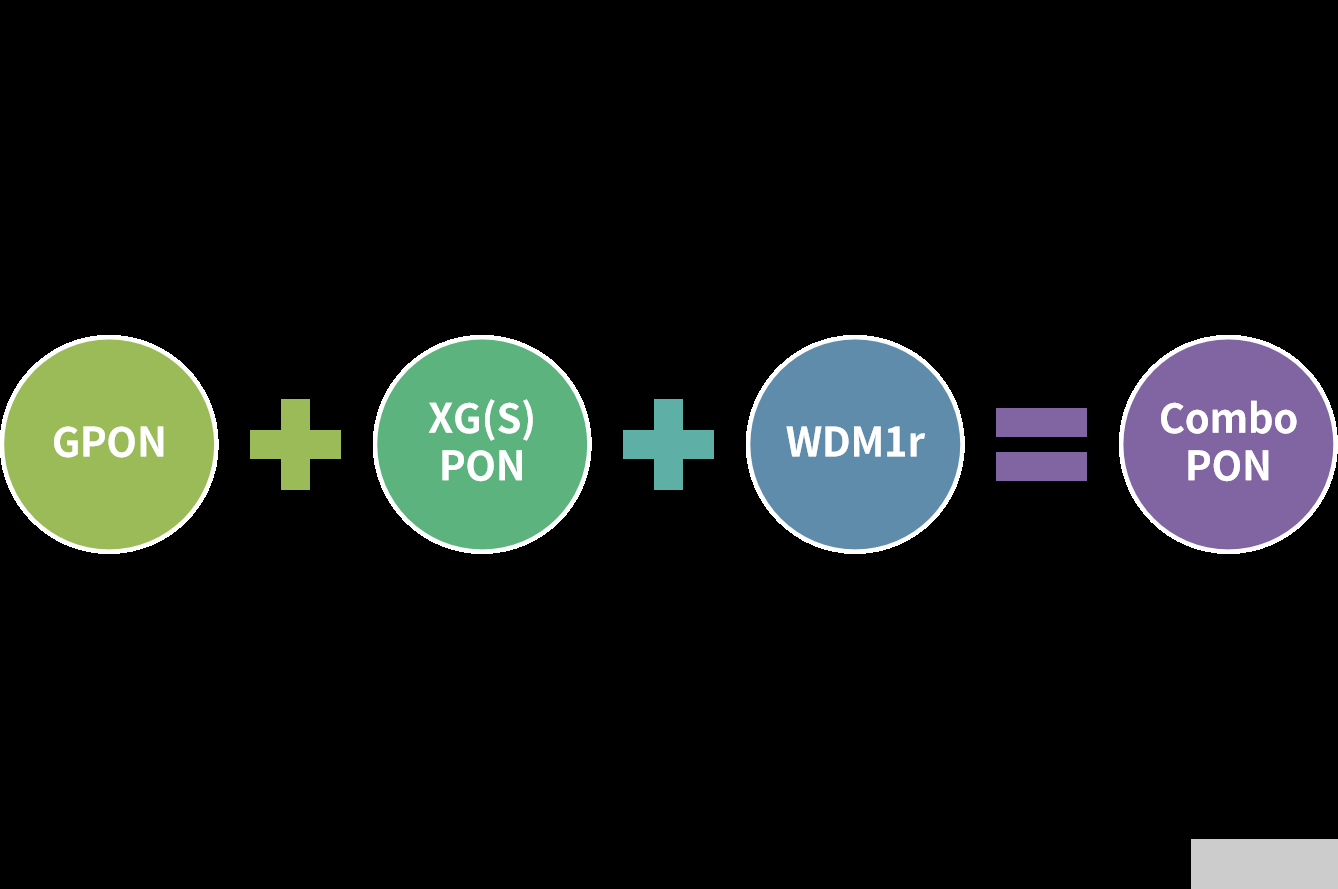
Introduction to Combo PON
In addition to the above three PON network protocols, "Combo PON" is also common. Combo PON is a PON network that supports multiple PON protocols. Currently, it generally refers to Combo PON of XG(S)-PON&GPON.
Technical principle:
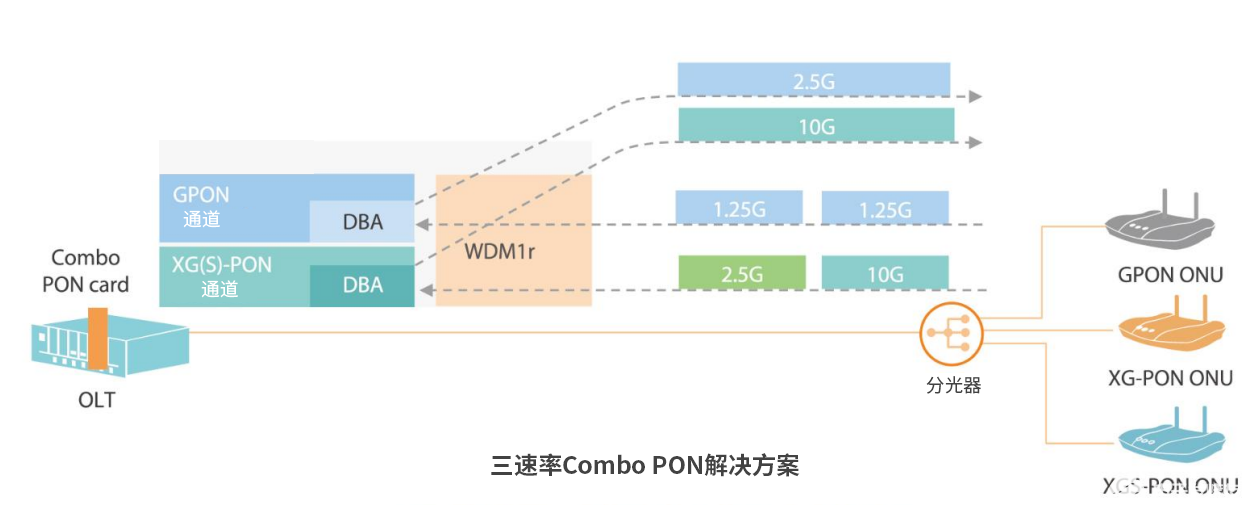
The Combo PON solution of XGS-PON & GPON is a built-in multiplexing solution that supports the coexistence of XGS-PON/XG-PON/GPON three modes. It is also called "tri-rate Combo PON" in the industry and is recognized by the industry as the evolution from GPON to XGS-PON. The best solution for smooth upgrades.
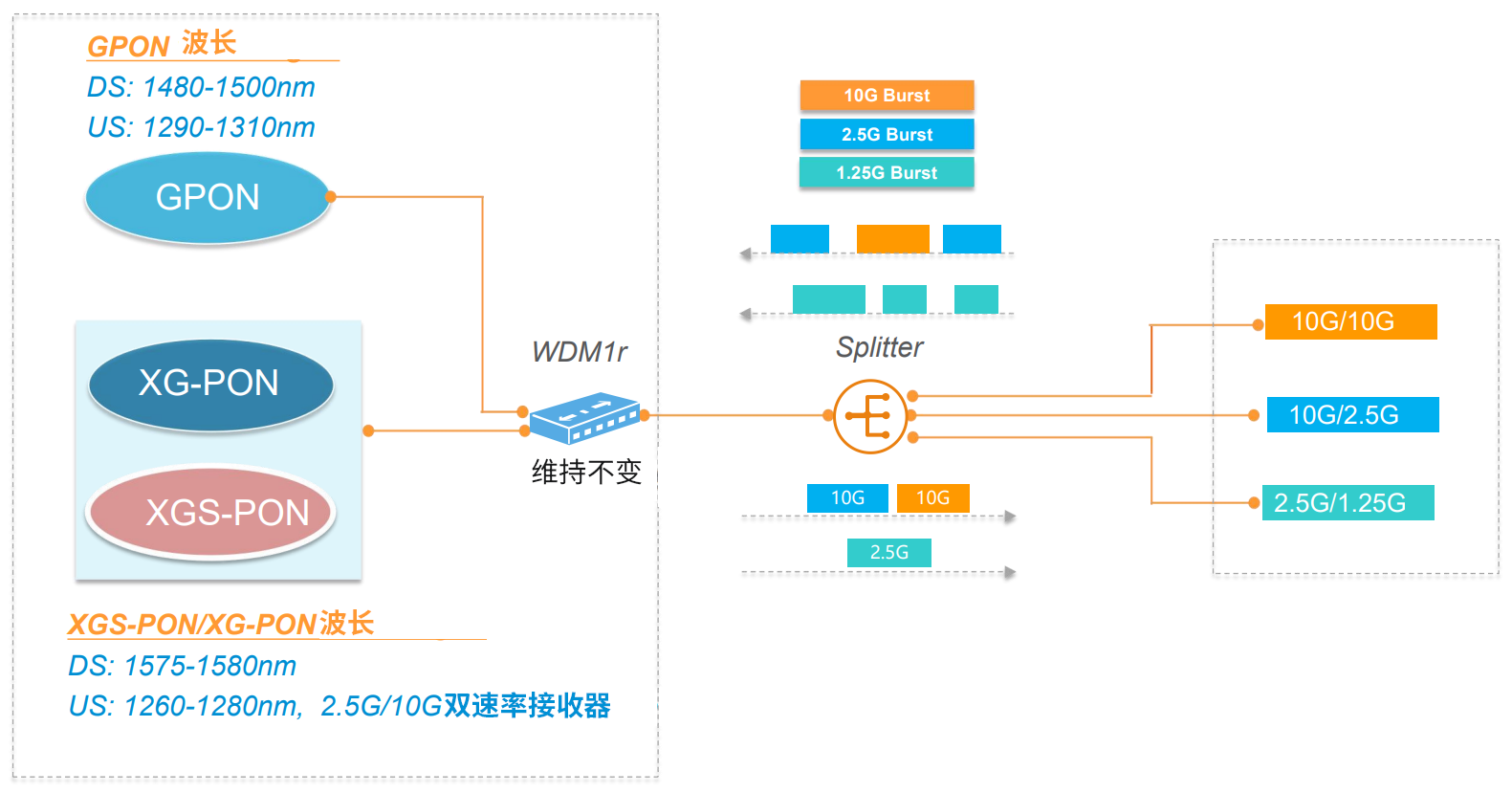
Combo PON technology realizes two-in-one GPON and XG(S)-PON ports, and three-in-one GPON, XG(S)-PON and WDM1r optical modules.
Advantage:
The optical power is consistent and ODN does not need to be modified.
Smooth evolution and investment protection
Terminal unified number, automatic identification
No need to take up additional space and resources
This not only allows coexistence between GPON and XG/XGS-PON OLT, but also allows coexistence between ONUs of various generations, thereby achieving smooth migration without modifying the ODN.
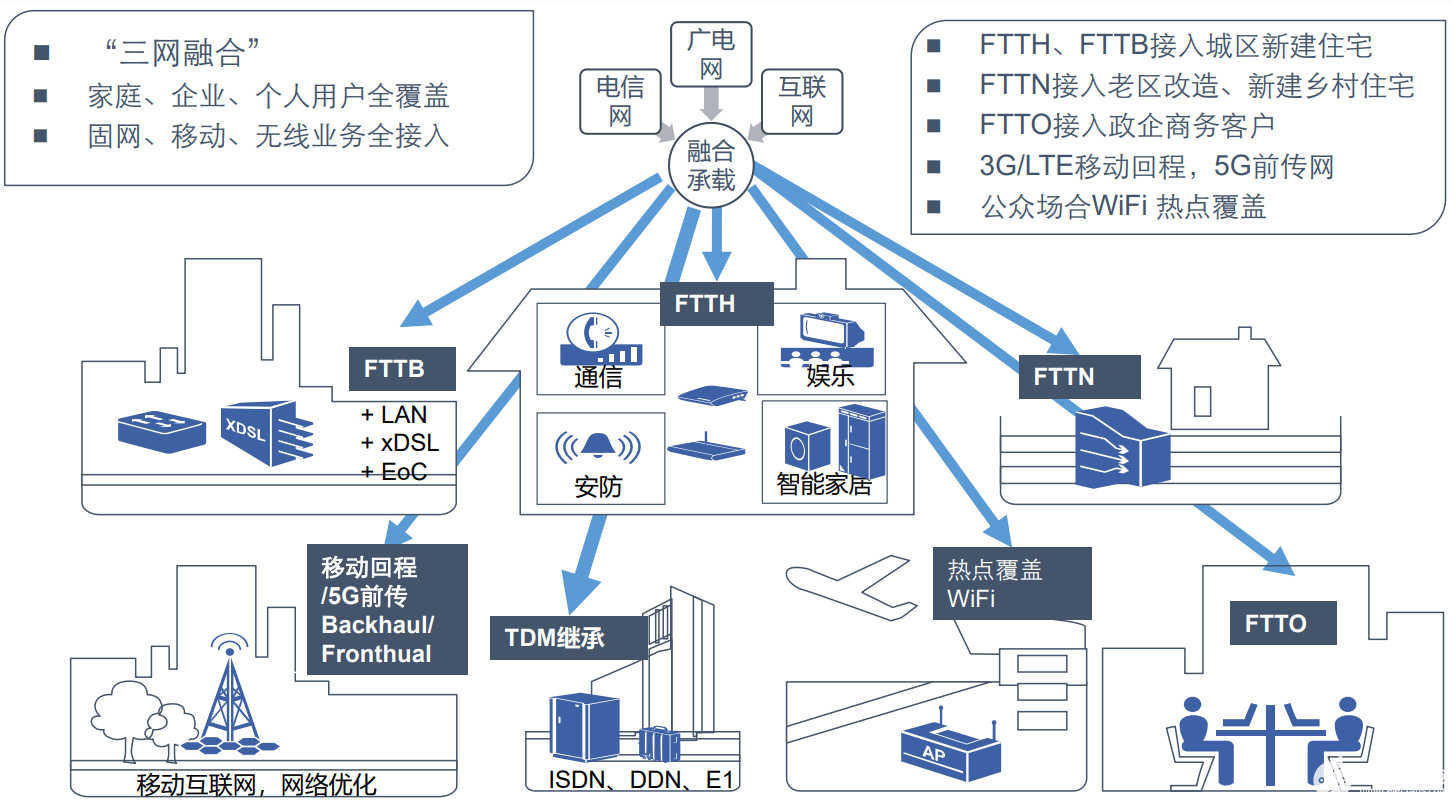
Typical application scenarios of PON
Definition of noun:
PON - Passive Optical Network
OLT - optical line terminal
ODN - optical distribution network
POS——Passive optical splitter
ONU/T——Optical network unit/terminal
Passive optical network refers to: The so-called "passive" means that (in the optical distribution network) it does not contain any electronic devices and electronic power supplies. ODN is entirely composed of passive components such as optical splitters (Splitters). Requires expensive active electronics.
Symmetry refers to: Symmetry in the PON network refers to whether the uplink and downlink rates provided by the PON port of the OLT are equal. If they are equal, it is symmetrical.
PON network support distance: optical fiber distance from the PON port of the OLT to the ONU
 The Difference Between AX1800 ONU and AX3000 ONU
The Difference Between AX1800 ONU and AX3000 ONU
 How are Huawei OLTs Classified?
How are Huawei OLTs Classified?
 The Future Trend of Optical Line Terminals (OLTs)
The Future Trend of Optical Line Terminals (OLTs)
 The Difference Between ONU and ONT
The Difference Between ONU and ONT